Cancer Risks, Warning Signs, Symptoms, Assessments, Management, and Other Facts.
Cancer remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide, affecting millions of individuals and their families. While the disease is complex and multifaceted, understanding cancer risks, warning signs, symptoms, assessments, and management strategies can empower individuals to take proactive steps in their health journey. This comprehensive overview aims to illuminate these aspects of cancer, fostering awareness and early intervention.
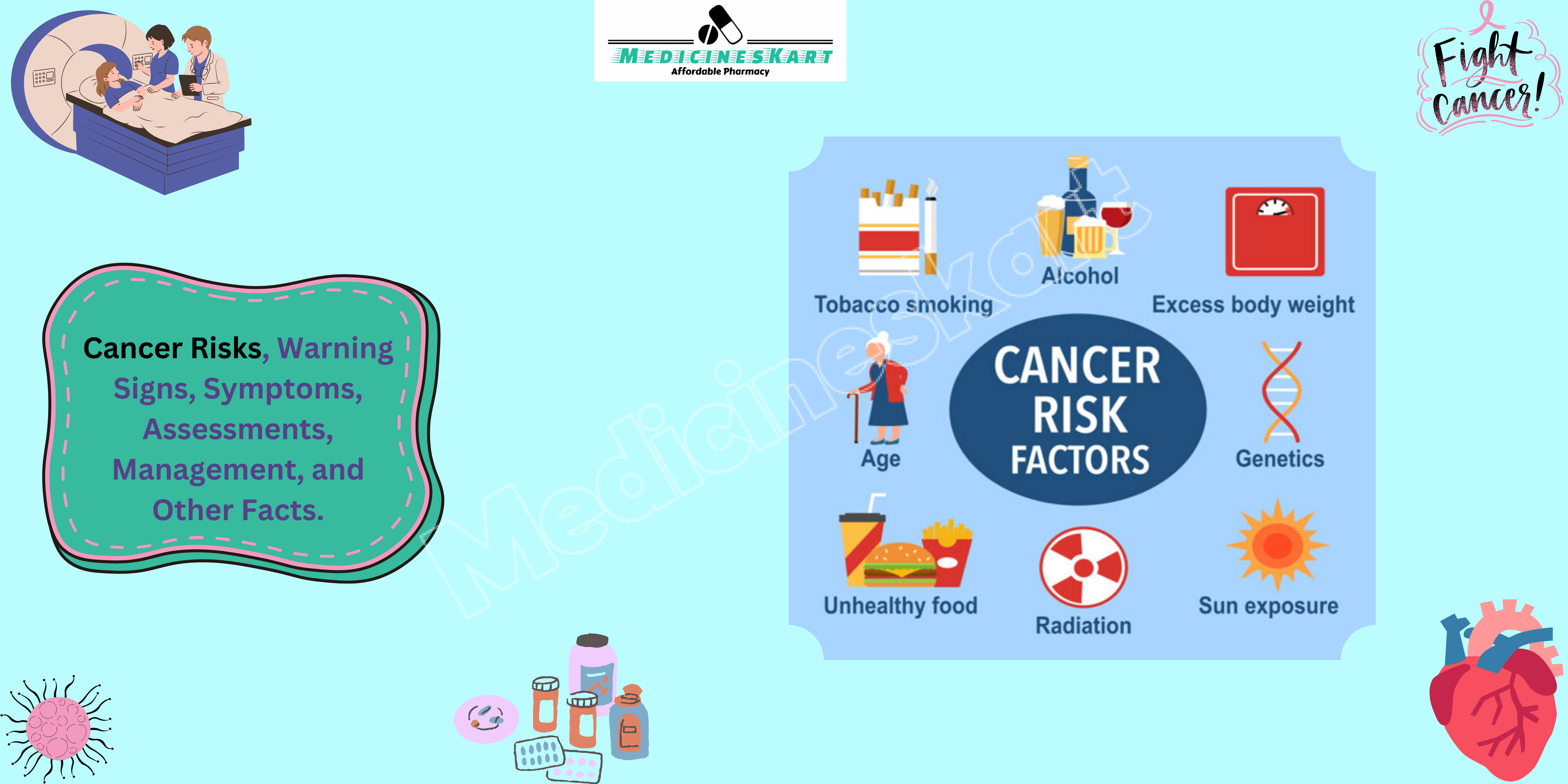
Understanding Cancer Risks
Cancer risk factors are characteristics or behaviors that increase the likelihood of developing cancer. They can be classified into two main categories: modifiable and non-modifiable.
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
- Age: The risk of developing cancer increases with age. Most cancers are diagnosed in individuals over the age of 50.
- Genetics: A family history of cancer can elevate the risk due to inherited genetic mutations. Certain genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, are linked to breast and ovarian cancer.
- Gender: Some cancers are gender-specific, such as prostate cancer in men and breast cancer in women.
- Ethnicity and Race: Certain ethnic groups have a higher prevalence of specific cancers due to genetic predispositions or lifestyle factors.
Modifiable Risk Factors
- Tobacco Use: Smoking and the use of tobacco products are the leading causes of cancer and cancer-related deaths, particularly lung cancer. Even secondhand smoke poses significant risks.
- Diet and Obesity: Poor dietary choices and obesity can increase the risk of several cancers, including colorectal, breast, and endometrial cancers. A diet high in processed foods, red meats, and low in fruits and vegetables can be particularly harmful.
- Physical Inactivity: Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and lowers cancer risk. Sedentary lifestyles are associated with increased cancer risk.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake is linked to various cancers, including liver, breast, and colorectal cancer. Limiting alcohol can mitigate this risk.
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun increases the risk of skin cancers, including melanoma. Protective measures against UV exposure are essential.
Warning Signs and Symptoms of Cancer
Early detection of cancer can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Being aware of warning signs and symptoms is crucial for prompt medical evaluation. While specific symptoms may vary based on the cancer type, some general warning signs include:
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant weight loss without trying can be an early sign of cancer.
- Fatigue: Persistent fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest may indicate an underlying health issue, including cancer.
- Pain: Unexplained or persistent pain, particularly if it doesn’t respond to treatment, warrants further investigation.
- Skin Changes: Changes in the appearance of moles or the development of new growths on the skin can be indicative of skin cancer.
- Changes in Bowel or Bladder Habits: Persistent changes, such as diarrhea, constipation, or blood in the urine, can signal cancers affecting the gastrointestinal tract or urinary system.
- Unexplained Bleeding: Any unusual bleeding, such as coughing up blood or blood in stool, should prompt immediate medical attention.
- Lumps or Swelling: The appearance of lumps or swelling in any part of the body may be a sign of cancer, especially if persistent.
- Persistent Cough: A cough that lasts more than a few weeks or worsens can be a warning sign of lung cancer.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Trouble swallowing or persistent indigestion may indicate esophageal or throat cancer.
Cancer Assessments
Prompt assessment and diagnosis are critical in the fight against cancer. Various screening and diagnostic tools are employed to detect cancer early:
- Screening Tests: Regular screenings can help identify cancers before symptoms appear. Common screenings include:
- Mammograms: For breast cancer
- Pap Smears: For cervical cancer
- Colonoscopy: For colorectal cancer
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: For prostate cancer
- Diagnostic Imaging: Imaging techniques, such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds, help visualize internal organs and identify tumors.
- Biopsies: A biopsy involves taking a sample of tissue for laboratory analysis to determine the presence of cancerous cells.
- Blood Tests: Certain blood tests can help assess overall health and detect specific markers associated with various cancers.
Cancer Management Strategies
Once diagnosed, cancer management involves a multidisciplinary approach tailored to the individual’s needs. Common management strategies include:
- Surgery: Surgical intervention aims to remove the tumor and surrounding tissue. It may be curative or palliative, depending on the cancer stage.
- Chemotherapy: This treatment uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. It may be used as the primary treatment or in conjunction with surgery or radiation therapy.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It can be employed before surgery to shrink tumors or after surgery to eliminate remaining cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: This innovative treatment harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It can be particularly effective in certain types of cancers, such as melanoma and lung cancer.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapies focus on specific molecules involved in cancer growth and progression, providing a more personalized treatment approach.
- Hormonal Therapy: For cancers influenced by hormones, such as breast and prostate cancer, hormonal therapies can help block hormone production or action.
- Palliative Care: Palliative care aims to enhance the quality of life for patients by managing symptoms and side effects, regardless of the cancer stage.
Coping with a Cancer Diagnosis
A cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming for patients and their families. Emotional and psychological support is vital during this challenging time:
- Seek Support: Joining support groups or engaging in counseling can provide emotional relief and connection with others experiencing similar challenges.
- Communicate with Healthcare Providers: Open communication with healthcare providers about concerns and treatment options can alleviate anxiety and improve understanding.
- Educate Yourself: Understanding the specific type of cancer and treatment options empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eating well, exercising, and prioritizing mental health can enhance overall well-being and resilience during treatment.
- Consider Integrative Therapies: Complementary therapies such as acupuncture, yoga, or meditation can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Additional Facts About Cancer
- Prevention: While not all cancers can be prevented, certain lifestyle choices can significantly reduce risk. Quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and practicing sun safety are essential preventive measures.
- Genetic Testing: Individuals with a family history of cancer may benefit from genetic testing to assess their risk and consider preventive measures.
- Survivorship: Many individuals successfully overcome cancer and become survivors. Survivorship care plans are essential for monitoring long-term effects and ensuring a quality post-treatment life.
- Research and Advancements: Ongoing research continues to provide insights into cancer biology, treatment options, and prevention strategies. Staying informed about advancements can offer hope and options for patients.
Conclusion
Understanding cancer risks, warning signs, symptoms, assessments, and management strategies is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. By adopting preventive measures and maintaining awareness of changes in their bodies, individuals can take proactive steps in their health journey. Education, support, and communication with healthcare providers are vital components in navigating the complexities of cancer. As research progresses and treatment options expand, there is hope for improved outcomes and a better quality of life for those affected by cancer.


Leave a Reply